DESDEO is an open source framework for interactive multiobjective optimization methods. The framework contains implementations of both scalarization- and population-based methods interactive methods. There are currently no other software frameworks that focus solely on the the implementation of interactive multiobjective optimization methods.
The mission of DESDEO is to increase awareness of the benefits of interactive multiobjective optimization methods, make interactive methods openly available, and to function as the central hub for implementations of various interactive methods. Apart from existing methods, DESDEO offers various tools to facilitate the development of new methods and their application as well.
DESDEO is an open source project and everybody is welcome to contribute!
DESDEO offers various features that can facilitate the application and development of new interactive multiobjective optimization methods. Some of the key features include, but are not limited to:
Disclaimer: most of the features are available on the new version of desdeo.
WWW-NIMBUS is based on the ideas of centralized computing and distributed interface. With software operating on the Internet, no special requirements are set on the user’s computer. This means that the operating system used or the compilers available play no role. In other words, no software has to be downloaded and it is always the latest version that is used. Furthermore, a convenient and graphical user interface can be implemented with visualization possibilities.
The structure of the interactive NIMBUS algorithm does not limit the variety of its applications in the area of multiobjective optimization. The only limiting factor in practice is the underlying single objective optimizer that has to be able to handle the subproblems and the possible special features of the problem to be solved.
The IND-NIMBUS system is capable of solving nonlinear multiobjective optimization problems involving even nondifferentiable and nonconvex functions where the variables can be continuous or integer-valued. It can be used in both MS-Windows and Linux operating systems and it has been designed so that it can be connected to different modelling and simulation tools. In this way, it can be used when solving complicated real-world problems that do not have explicit function formulations but function values come, for example, from the solution of a system of partial differential equations.
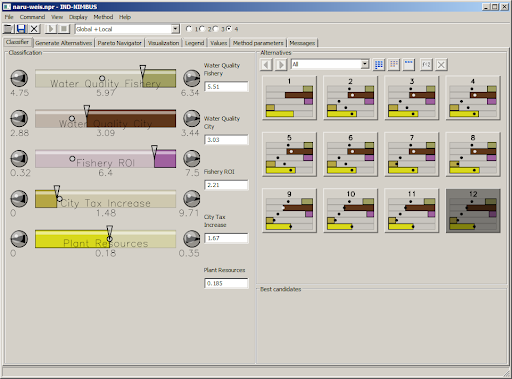
The basic setting in IND-NIMBUS is the same as in WWW-NIMBUS but the user interface is completely different. The IND-NIMBUS user interface has been built with the wxPython toolset and there exists a high-level NIMBUS GUI framework where different parts of the user interface have been isolated as independent components.
After the optimization problem has been specified, the system generates a Pareto optimal neutral compromise solution as a starting point or the solution given by the decision maker is projected onto the Pareto optimal set. This point is the basis of the first classification. This solution is shown to the decision maker as a bar chart where each bar stands for one of the objective functions. The classification of the objective functions can be carried out by indicating desirable values in a bar chart with a mouse. The bars include information about the current objective values with colours as well as the estimated ranges of each objective function in the Pareto optimal set as the end points of the bars. The less colour one can see in the bar, the closer the current value is to the ideal one and, thus, the better it is.
Mattilanniemi 2 (Agora building), Jyväskylä, Finland
optim@jyu.fi
Copyright © Multiobjective Optimization Group all rights reserved.